32.5 Progressive Picts and Slides
32.5.1 Progressive Picts
A progressive pict or “ppict” is a kind of pict
that has an associated “pict placer,” which generally represents a
position and alignment. New picts can be placed on the progressive
pict by calling ppict-add, and the placer can be updated by
calling ppict-go. The ppict-do form provides a
compact notation for sequences of those two operations.
| (ppict-do base-expr ppict-do-fragment ...) |
|
| (ppict-do* base-expr ppic-do-fragment ...) | | | | ppict-do-fragment | | = | | #:go placer-expr | | | | | | | #:set pict-expr | | | | | | | #:next | | | | | | | #:alt (ppict-do-fragment ...) | | | | | | | elem-expr |
| | | |
|
Builds a pict (and optionally a list of intermediate picts)
progressively. The
ppict-do form returns only the final pict;
any uses of
#:next are ignored. The
ppict-do* form
returns two values: the final pict and a list of all partial picts
emitted due to
#:next (the final pict is not included).
A #:go fragment changes the current placer. A #:set
fragment replaces the current pict state altogether with a new
computed pict. A #:next fragment saves a pict including only
the contents emitted so far (but whose alignment takes into account
picts yet to come). A #:alt fragment saves the current pict
state, executes the sub-sequence that follows, saves the result (as if
the sub-sequence ended with #:next), then restores the saved
pict state before continuing.
The elem-exprs are interpreted by the current placer. A
numeric elem-expr usually represents a spacing change, but
some placers do not support them. A spacing change only affects added
picts up until the next placer is installed; when a new placer is
installed, the spacing is reset, usually to 0.
The ppict-do-state form tracks the current state of the
pict. It is updated before a #:go or #:set fragment
or before a sequence of elem-exprs. It is not updated in the
middle of a chain of elem-exprs, however.
Examples: |
| | > base | 
|
|
The use of
ppict-do in the defnition of
base above
is equivalent to
Examples: |
| | > circles-down-1 | 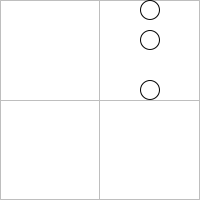
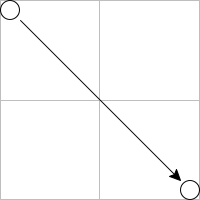
| | | > (inset circles-down-2 20) ; draws outside its bounding box | 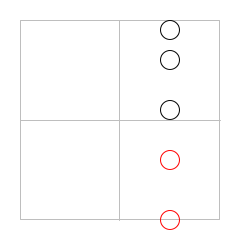
| | > (inset (clip circles-down-2) 20) | 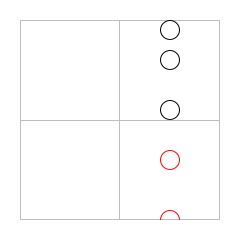
| | 
| | '(   ) ) |
|
More examples of ppict-do are scattered throughout this
section.
Creates a new pict by adding each
elem pict on top of
pp according to
pp’s placer. The result pict may or
may not be a
progressive pict, depending on the placer used.
An elem that is a real number changes the spacing for
subsequent additions. A elem that is #f is
discarded; it is permitted as a convenience for conditionally
including sub-picts. Note that #f is not equivalent to
(blank 0), since the latter will cause spacing to be added
around it.
Returns #t if x is a placer, #f otherwise.
Returns #t if x is a placer based on a reference
point, #f otherwise.
Returns a placer that places picts according to
rel-x and
rel-y, which are interpeted as fractions of the width and
height of the base
progressive pict. That is,
0,
0 is the top left corner of the base’s bounding box, and
1,
1 is the bottom right. Then
abs-x and
abs-y offsets are added to get the final reference point.
Additions are aligned according to align, a symbol whose name
consists of a horizontal alignment character followed by a vertical
alignment character. For example, if align is 'lt,
the pict is placed so that its left-top corner is at the reference
point; if align is 'rc, the pict is placed so that
the center of its bounding box’s right edge coincides with the
reference point.
By default, if there are multiple picts to be placed, they are
vertically appended, aligned according to the horizontal component of
align. For example, if align is 'cc, the
default composer is vc-append; for 'lt, the
default composer is vl-append. The spacing is
initially 0.
Examples: |
| 
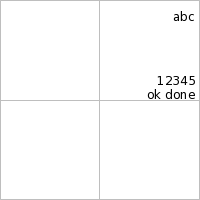
| | > (ppict-do base | | #:go (coord 1 0 'rt #:abs-x -5 #:abs-y 10) | | 50 ; change spacing | | (text "abc") | | (text "12345") | | 0 ; and again | | (text "ok done")) |
| 
| | 
|
|
Returns a placer that places picts according to a position in a
virtual grid. The row and col indexes are numbered
starting at 1.
Uses of grid can be translated into uses of coord,
but the translation depends on the alignment. For example,
(grid 2 2 1 1 'lt) is equivalent to (coord 0 0 'lt),
but (grid 2 2 1 1 'rt) is equivalent to (coord 1/2 0 'rt).
Examples: |
| | > none-for-me-thanks | 
| | 
|
|
Returns a placer that places picts by evenly spreading them diagonally
across the base pict in “cascade” style. This placer does not
support changing the spacing by including a real number within the
pict sequence.
When a list picts is to be placed, their bounding boxes are normalized
to the maximum width and height of all picts in the list; each pict is
centered in its new bounding box. The picts are then cascaded so there
is step-x space between each of the picts’ left edges; there
is also step-x space between the base pict’s left edge and
the first pict’s left edge. Similarly for step-y and the
vertical spacing.
If step-x or step-y is 'auto, the spacing
between the centers of the picts to be placed is determined
automatically so that the inter-pict spacing is the same as the
spacing between the last pict and the base.
Returns a placer that places picts by tiling them in a grid
cols columns wide and rows rows high.
Returns a placer that places picts according to a reference point
based on an existing pict within the base.
Returns a placer like x-placer except that the y-coordinate of its
reference point is computed by y-placer.
32.5.1.1 Tagging picts
Returns a pict like
p that carries a symbolic tag. The tag
can be used with
find-tag to locate the pict.
Locates a sub-pict of
p. Returns a pict-path that can be used
with functions like
lt-find, etc.
Returns #t if x is a symbol or a non-empty list of
symbols, #f otherwise.
32.5.2 Progressive Slides
| (pslide ppict-do-fragment ...) |
Note that like slide but unlike ppict-do*, the
number of slides produced is one greater than the number of
#:next uses; that is, a slide is created for the final pict.
Remember to include gap-size after updating the current
placer if you want slide-like spacing.
Example: |
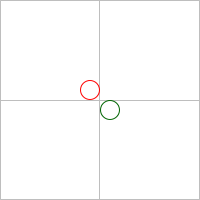
| > (pslide #:go (coord 0 0 'lt) | | (t "You do not like") | | (colorize (t "green eggs and ham?") "darkgreen") | | #:next | | #:go (coord 1 1 'rb) | | (colorize (t "I do not like them,") "red") | | (t "Sam-I-am.")) |
| 
|
|
Note that the text is not flush against the sides of the slide,
because pslide uses a base pict the size of the client
area, excluding the margins.
Controls the initial pict used by
pslide. The default value
is
Controls the initial placer used by
pslide. The default value
is







 )
)